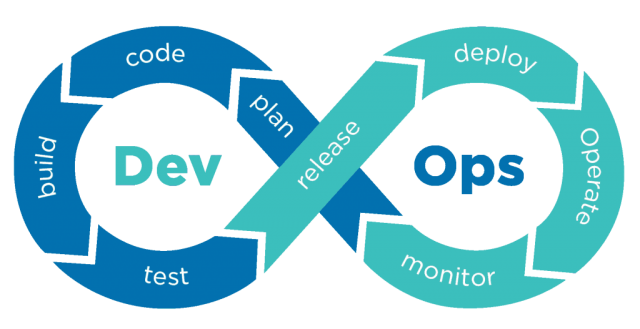
At Redefine, we evaluate your organization’s needs and goals together in our DevOps consulting services to identify the maturity steps you need to follow. Through phased planning aimed at these goals, we enhance your organization’s DevOps awareness and culture, supporting you in applying standard and up-to-date approaches in methods and tools.
Continuous Integration (CI) is a method used to ensure that the system remains functional after changes are made to the code and that these changes do not introduce any issues. Unit tests are employed to detect problems and breaks. Since the changes made are part of a new build, any errors that occur in the tests indicate that the changes have broken the system. In such cases, all programmers are notified to ensure that the error is resolved as quickly as possible. Continuous integration ensures that a working version is always available as a result of the efforts made by programmers on the code.
Continuous Integration (CI) helps developers to integrate their code more frequently. When developers merge changes into an application, these changes are verified by automatically building the application and conducting various levels of tests to ensure that they do not break the application.